Multifunctional drying unit with blades Multifunctional Drying Unit With Blades,Automatic Vacuum Dryer,Multifunctional Drying Unit,Rotary Vacuum Dryer Wuxi Zhanghua Pharmaceutical Equipment Co. Ltd , https://www.wx-zhanghua.com
Key words: dynamic metering, flow meter coefficient, pure oil, crude oil working pressure, continuity of oil delivery, large amount of delivery, crude oil is generally in a fluid or semi-fluid state, and has compressibility. As with other fluids, temperature changes will inevitably cause volume changes, and the compressibility of crude oil will determine the effect of pressure on volume. In the verification work of the flowmeter, the temperature is also the main factor that affects the change of the flowmeter coefficient. Although the pressure has an influence, it is smaller than the temperature. Regardless of size, it is directly related to the economic benefits of both parties. These issues should cause us to pay enough attention to the work of the measurement transfer workers.
First, the impact of temperature and pressure on the calculation of oil volume (A) the impact of temperature on the calculation of oil volume At present, China's dynamic measurement standards mainly implement GB9109.1-88 "general principles of dynamic measurement of crude oil", GB9109.5-88 "oil dynamics Calculate the oil volume calculation and GB/T1885-1998 Oil Meter. In GB 9019.5-88 "Dynamic oil measurement of crude oil", it is stipulated that when calculating the oil volume, the volume of crude oil is converted into standard volume at the measurement temperature. The standard volume of crude oil (V20) can be obtained by multiplying the volume (Vt) at the crude oil metering temperature and the temperature volume correction coefficient (Cti). That is: V20=Vt•Cti=Cti=V20/Vt=Ït/Ï20=[Ï20−υ(t−20)]/Ï20=1−[Ï…(t−20)]/Ï20 The crude oil temperature volume is known from the above equation. The relationship between the correction coefficient Cti and the crude oil temperature t is linearly decreasing, and the Cti value decreases as the crude oil temperature increases. Daqing crude oil is a highly viscous and easily condensable crude oil, generally used hot oil pipeline transmission, the external transmission temperature is generally between 30 °C ~ 50 °C, when the calculation of the fuel should take Cti ≤ 1; when t ≤ 20 °C, there Cti ≥ 1, Russian crude oil has a low freezing point, the delivery temperature is sometimes less than 20°C, and Cti>1 should be taken for the calculation of the oil amount.
(B) The impact of pressure on the calculation of oil volume The volume of crude oil and liquid petroleum products varies with pressure and generally decreases with increasing pressure. Under certain pressure, the change of the volume of the oil with relatively large density is relatively small, and the volume change of the oil is larger.
The relationship between crude oil pressure and volume can be expressed as:
Vpt=Ve×[1-F×(Pt-Pe)] 
When calculating the oil volume, the crude oil volume must be corrected to standard condition pressure to obtain the crude oil standard volume V20.
Relationship between pressure correction coefficient (Cpi) and compression factor (F):
Cpi=1/[1-(Pt-Pe)×F]
In the formula:
Cpi - crude oil volume pressure correction factor;
F - compressibility of petroleum and liquid petroleum products;
kPa-1Pt - Pressure under crude oil metering, °C;
Pe—saturated vapor pressure of crude oil. When the saturated vapor pressure is not greater than 101.325 kPa at the metering temperature, set Pe=0. From the above equation, the Cpi value increases with pressure.
Second, the impact of temperature and pressure on the verification of the flow meter At present, in domestic crude oil metering and delivery methods, the use of flow meter as the main apparatus of the dynamic measurement has dominated. According to the dynamic measurement implementation standards GB9109.1-88 "general principles for dynamic measurement of crude oil" and GB9109.5-88 "calculation of crude oil dynamic measurement," the provisions of the original volume measurement, the main flow meter coefficient of oil and flow meter Two kinds of error delivery methods, in theory, the flow meter coefficient oil delivery method is more accurate, reasonable and fair.
According to the actual operation of the flowmeter, the flowmeter should be tested regularly, the basic errors should be handled properly, and the flowmeter coefficient should be adjusted in time. However, due to the limitation of the production process, the oil temperature and pressure at the time of checking the flowmeter are different from the oil temperature and pressure at the time of production operation. Among them, temperature is the main factor affecting the change of flowmeter coefficient. Although pressure has influence, it has little influence on the flowmeter coefficient. Therefore, the temperature and pressure of the test and production run should be consistent as much as possible, and adjustment should be made when the difference is large. Eliminate the resulting error. The current standard used for flow meter verification is JJG667-1997 "Liquid Volume Flowmeter Verification Regulations."
An external metering station uses a standard volumetric tube on-line to check the flowmeter. The specific parameters of the standard volumetric tube are as follows: inner diameter D=358.0mm; wall thickness e=10mm; volumetric tube expansion coefficient βs=3.33×10-11-6°C-1 Volume tube material elastic modulus ES=2.04×10-11Pa; number β=780×10-6°C-1; original standard density Ï20=855.2kg/m3; liquid (crude oil) compression coefficient κ=0.847×10- 6kPa-1; flowmeter operating temperature value tm = 40.5 °C; flowmeter working pressure Pm = 0.32MPa; standard volume tube working temperature te = 40.3 °C; volume tube working pressure Ps = 0.30MPa; if the operating temperature rises 1 °C, The working pressure rises by 0.1MPa. How does the flowmeter coefficient change? Calculated according to the crude oil 1000×104t delivered by the metering station outside the country, how does the temperature and pressure change affect the oil volume? 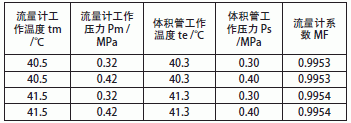
3. Conclusion In summary, in the dynamic measurement of crude oil, both the calculation of the standard volume of crude oil and the verification of the flow meter coefficient, the temperature and pressure are two key parameters that cannot be ignored. No matter what the impact on one side will eventually be attributed to the settlement of pure oil, affecting the economic benefits of both parties.
The influence of temperature and pressure on the calculation of dynamic metering oil
Abstract: In the dynamic measurement of crude oil, temperature and pressure are two important parameters, which not only directly affect the standard volume calculation of crude oil, but also play an important role in the verification of the flowmeter. Both the crude oil standard volume and the flowmeter verification work will eventually affect the pure oil volume settlement, which will affect the economic benefits of both crude oil transfer parties.
In the formula:
Table 1 Changes in Flow Meter Coefficients with Degree and Pressure Changes
As can be seen from Table 1, the influence of temperature on the verification work is more significant than the pressure. When the flow meter coefficient is MF = 0.9953, the crude oil is transported 1000 × 104t outside the year, and when the temperature and pressure change, MF = 0.9954, according to GB9109.5-88 "Dynamic oil measurement of the crude oil" rule ma = Vi • Ï20 • ( MF • Cpi • Cti • Fa • Cw). At this time, ma = 1000.1031 × 104t, the difference between the crude oil exported is Δma = 1031t. It can be seen that the true values ​​of temperature and pressure in the flowmeter verification are extremely important. Therefore, in order to obtain the true temperature and pressure value and improve the reliability of the verification result of the flowmeter, the flowmeter should be run as far as possible in the verification environment in the normal work; the temperature field and the pressure field should be in a stable state as soon as possible.