Hand Disinfectant Gel,Alcoholic Hand Gel,Alcohol Gel Hand Sanitizer,Instant Hand Sanitizer Gel Henan Diyi Medical Technology Development Co.,Ltd. , https://www.diyimedical.com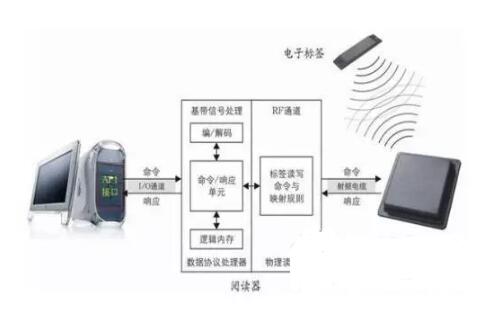
Principles of Radio Frequency Technology and Sixteen Applications
Radio Frequency (RF) is an abbreviation of Radio Frequency. The more common applications are radio frequency identification (RFID), often called inductive electronic chip or proximity card, proximity card, contactless card, electronic tag, electronic bar code and so on. The principle is that the scanner emits radio wave energy of a specific frequency to the receiver to drive the receiver circuit to send the internal code, and the scanner receives the code. The special features of the receiver are battery-free, contact-free, card-free, and dirt-free, and the chip password is the only one in the world that cannot be duplicated, with high security and long life. The application of RFID is very extensive. At present, typical applications include animal wafers, car wafer anti-theft devices, access control, parking lot control, production line automation, and material management. There are two types of RFID tags: active tags and passive tags.
RF technology works
The basic model of the radio frequency identification system is shown in the figure.
Among them, electronic tags are also called radio frequency tags, transponders, and data carriers; readers are also called readout devices, scanners, communicators, and readers (depending on whether the electronic tag can wirelessly overwrite data). Between the electronic tag and the reader, a coupling element is used to realize the spatial (non-contact) coupling of the RF signal in the coupling channel, and energy transfer and data exchange are realized according to the timing relationship.
There are two types of coupling of RF signals that occur between the reader and the RFID tag.
(1) Inductive coupling. Transformer model, through the spatial high-frequency alternating magnetic field to achieve coupling, based on the law of electromagnetic induction, as shown:
(2) Electromagnetic backscatter coupling: Radar principle model, electromagnetic waves emitted, hitting the target and reflecting, and carrying back the target information, based on the spatial propagation of electromagnetic waves
The inductive coupling method is generally suitable for low-frequency, high-frequency short-range radio frequency identification systems. Typical operating frequencies are: 125kHz, 225kHz, and 13.56MHz. The recognition distance is less than 1m and the typical action distance is 10-20cm.
The electromagnetic backscatter coupling method is generally suitable for long-range radio frequency identification systems for UHF and microwave work. Typical operating frequencies are: 433MHz, 915MHz, 2.45GHz, 5.8GHz. Identification of the role of distance greater than 1m, a typical role of the distance 3 - l0m
RF Technology Applications
1. Logistics: Tracking of goods during logistics, automatic collection of information, storage applications, port applications, postal services, express delivery
2. Retail: real-time statistics of merchandise sales, replenishment, security
3. Manufacturing: Real-time monitoring of production data, quality tracking, automated production
4. Garment industry: automated production, warehouse management, brand management, single product management, channel management
5. Medical: Medical Device Management, Patient Identification, Baby Theft Prevention
6, identification: electronic passports, ID cards, student ID cards and other electronic documents.
7, anti-counterfeiting: Anti-counterfeiting of valuables (smoke, alcohol, drugs), ticket security, etc.
8. Asset Management: Assets of various types (valuable or large quantities of similarity or dangerous goods, etc.)
9. Transportation: High speed non-stop, taxi management, bus hub management, railway locomotive identification, etc.
10. Food: Freshness management of fruits, vegetables, fresh food, food, etc.
11, animal identification: training animals, animal husbandry, pets, and other identification management
12. Library: Bookstores, libraries, publishers, etc.
13. Automobile: Manufacturing, Anti-theft, Positioning, Car Keys
14. Aviation: Manufacturing, passenger ticket, baggage tracking
15. Military: Identification and tracking of ammunition, guns, supplies, personnel, trucks, etc.
16. Electricity: Intelligent power inspection, smart meter reading and power asset management