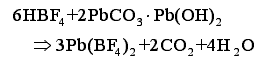Study on Electroplating Lead Technology of Lead-acid Battery Negative Grid Copper Network Abstract: The lead-acid battery anode screen grid copper plating process was introduced. The pretreatment and electroplating technology of copper grid before electroplating was discussed to improve product quality and achieve high efficiency and low energy consumption. 1. Copper network pretreatment 1.1 Degreasing In the process of production and molding of copper net, the surface is contaminated with oily materials. It must be degreased (ie degreased) firstly during electroplating. Otherwise, it is difficult to plate lead when plating, or the bonding strength of plating is easy to fall off. Commonly used degreasing methods include chemical degreasing, organic solvent degreasing, electrochemical degreasing, wiping degreasing, and ultrasonic degreasing. Chemical degreasing is the removal of saponified fats and oils by saponification and emulsification of fats and oils by hot alkali liquor, and removal of non-saponified fats and oils by emulsification of surfactants. The sodium hydroxide content in the lye should not be too high. Alkaline degreasing can only saponify animal and vegetable oils. If the copper net contains mineral oil, it must be added with surfactant such as soap powder and OP emulsifier to remove it. Ultrasonic degreasing is a machine that uses ultrasonic vibration to generate tens of thousands of small bubbles in the degreasing liquid. When the production and closure are formed, strong mechanical force is generated, and the grease and dirt adhering to the surface of the object are quickly detached, thereby accelerating the degreasing process. Degreasing is more thorough. When using ultrasonic degreasing, the temperature and concentration of the degreasing liquid should not be too high, otherwise it will hinder the propagation of ultrasonic waves and reduce the degreasing ability. Copper net degreasing uses a combination of lye degreasing and ultrasonic degreasing. The ultrasonic device is installed between the walls of the lye tank. The use of ultrasonic waves can reduce the concentration and temperature of the lye, which can save energy and protect the copper mesh from corrosion and degreasing effect. After the copper mesh is degreased, it must be thoroughly cleaned to avoid bringing the lye into the next process and affecting the etching effect. 1.2 etching After the copper mesh is degreased, it enters the etching process, and the etching can remove the oxide film and the rust on the copper mesh, thereby improving the bonding strength between the copper mesh substrate and the plating layer. The etching solution consists of sulfuric acid, nitric acid and hydrochloric acid. At room temperature, the sulfuric acid solution has a weaker ability to dissolve metal oxides, and the solution concentration is increased, and the etching ability of sulfuric acid cannot be significantly improved. Therefore, the volume concentration can be maintained at 200 to 250 mL/L. Hydrochloric acid has a strong chemical dissolution effect on metal oxide at room temperature, and the volume concentration is about 3 mL/L; nitric acid can effectively remove the heat-treated oxide scale on the copper mesh, and the concentration is generally 50-100 mL/L. The combination of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid gives the copper mesh a metallic luster. During use, nitric acid should be appropriately added according to the amount of loss and the etched light of the copper mesh to maintain its concentration. After the copper mesh is etched, it must be thoroughly cleaned by running water and pure water before it can be transferred to the electroplating process. 2. Preparation and composition requirements of fluoroborate lead plating solution 2.1 plating solution preparation First, a certain amount of pure water is injected into the plating solution preparation tank, and hydrofluoric acid is gradually added under stirring, and then boric acid is added in portions, and hydrofluoric acid and boric acid are reacted to form fluoroboric acid: In order to prevent precipitation of lead fluoride in the plating solution, free hydrofluoric acid cannot exist in the solution, so the boric acid should be excessive. Then slowly add lead oxide powder, stir well to make the reaction thoroughly, and produce lead fluoroborate: Or add basic lead carbonate to water to make a paste, slowly add fluoroboric acid to form lead fluoroborate under constant stirring: Allow to stand, filter, add pure water, adjust the density to a suitable level, add sodium lignin sulfonate or bone glue additive, stir evenly 2.2 plating composition requirements In order to make the coating crystal fine and ensure high current efficiency, in addition to maintaining the stable concentration of lead fluoroborate, the plating solution also contains a certain amount of free fluoroboric acid, free boric acid and rubber (or lignin) additives. The role of fluoroboric acid is to ensure the normal dissolution of PbO and lead anode, stabilize the lead fluoroborate in the solution, increase the conductivity of the solution, make the coating crystal fine, and reduce the formation of dendrites. Excess boric acid is present to prevent the formation of hydrogen fluoride, thereby avoiding the formation of a white precipitate of lead fluoride (PbF2), so that the lead anode strip is well dissolved and the plating solution is stable. A small amount of glue (or lignin) additive is mainly used to improve the crystallization of the coating. Insufficient additive content, rough coating, poor plating ability, poor deep plating ability, easy to produce dendrites; additive content is too high, the coating will produce streaks. The anode strip should be pure lead, and the content of bismuth, silver and copper should be as low as possible to avoid the formation of anode mud and rough coating. The fluoroborate lead plating solution is relatively stable, the anode dissolution and cathode precipitation are basically balanced, and the allowable range of lead ion content is wide, so the solution does not need to be adjusted frequently. Considering the loss of the copper mesh workpiece, it can be analyzed once a week or monthly according to the production situation. According to the analysis results, fluoroboric acid, boric acid and additives are appropriately added. When the production is stopped for a long time, the lead anode strip should be taken out to prevent the lead anode from being excessively dissolved, resulting in imbalance of the solution composition. The lead anode strip can be stored in clean water. 3. Hook and conductive contact In the copper plating process, the pre-plating pretreatment and plating solution are important for the quality of the plating. The influence of the hook and the conductive contact cannot be ignored. Hooks are an indispensable tool for electroplating. In copper mesh plating, there are two kinds of hooks, one is to connect the anode strip and the pole, and the other is to connect the copper mesh and the pole. The hooks must fix the copper mesh and the lead anode strip, and ensure that the current flows evenly through the copper mesh. The hook should be designed according to the characteristics of heavy and long lead anode, light copper wire and large area: it has sufficient mechanical strength and good electrical conductivity, firm contact, convenient loading and unloading, light weight, and should increase production efficiency as much as possible. Conductive contact generally refers to the contact of the hook with the pole, the contact of the hook with the anode strip, the contact of the hook with the copper mesh, etc. The conductive contact directly affects the current distribution, and the contact point should maintain the color of the copper, so that the resistance can be reduced. It can reduce uneven current distribution or non-conduction due to poor local contact. In particular, when the copper mesh has several pieces of parallel plating, if the conductive contact is not good, the current distribution is uneven, and the direct consequence is that the difference in the weight of the plating layer is caused. It is recommended to brush the conductive contact parts frequently and keep them clean. 4. Current and time The current and time during plating are primarily determined by the plating area, thickness, and operating efficiency requirements. The current density range is wide, generally between 1 and 3 A/dm3, and can be divided into 1 to 3 stages during actual operation. According to the actual production conditions, under the premise of ensuring the quality of the coating, the current and time can be adjusted appropriately to achieve optimization. 5. Conclusion Copper mesh plating is an important process in the production of large-capacity lead-acid batteries, and the process is determined by numerous trial and error studies. In production, we must pay attention to various technical parameters stipulated by the process and strengthen process management. To achieve three wins in product quality, economic efficiency and environmental benefits. Screen Printing Machine For Glass Bottles,Glass Bottle Screen Printing Machine,Screen Printing Machine For Glass,Glass Bottle Printer GIG (DONGGUAN) CO., LTD , https://www.tubeprinter.com![]()
![]()